
What is cervical dystonia?
Cervical dystonia (CD) is a condition that causes neck muscles to tighten or spasm, causing neck pain and making the head turn, pull in one direction, or shake. CD can even make activities of daily living a struggle, including walking and driving.

What is cervical dystonia?
Cervical dystonia (CD) is a condition that causes neck muscles to tighten or spasm, causing neck pain and making the head turn, pull in one direction, or shake. CD can even make activities of daily living a struggle, including walking and driving.

Janice has been compensated to share her experience.
Patient experience (Janice):
First symptoms or without treatment: “[By the time I was diagnosed,] the symptoms had progressed to a very obvious uncontrollable movement, … back and neck pain … Then the pain got worse from the constant muscle spasms, so it got really bad.”
Reappearance of symptoms between treatment injections can take a toll on you physically. When benefits from treatment wear off before the next injection, people with CD have reported disruptions in their ability to work, interact socially, drive, and even perform simple activities of daily living.
Signs & Symptoms
Are you experiencing the signs and symptoms of cervical dystonia?
Cervical dystonia, also called spasmodic torticollis, occurs when nerve signals tell the neck muscles to tighten or spasm. This can cause your head to shake or twist in a different direction. You may also feel severe pain and discomfort. The contractions may be continuous or occur as spasms. In some people, symptoms may seem to go away but are often recurring.
In adults with CD, the abnormal position of the head may vary, depending on the muscles that are affected, as shown below:
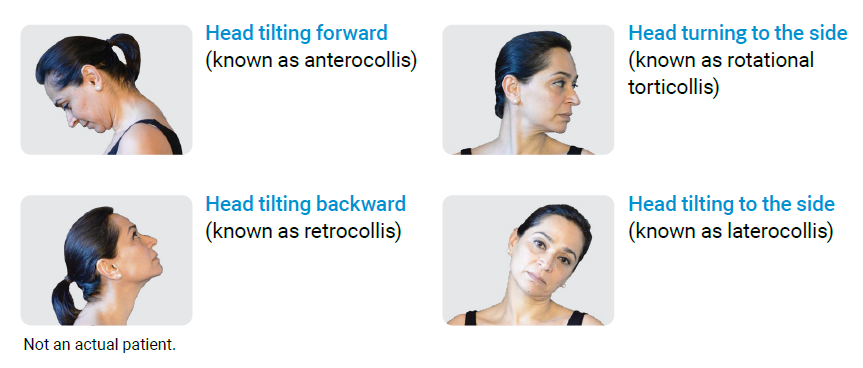
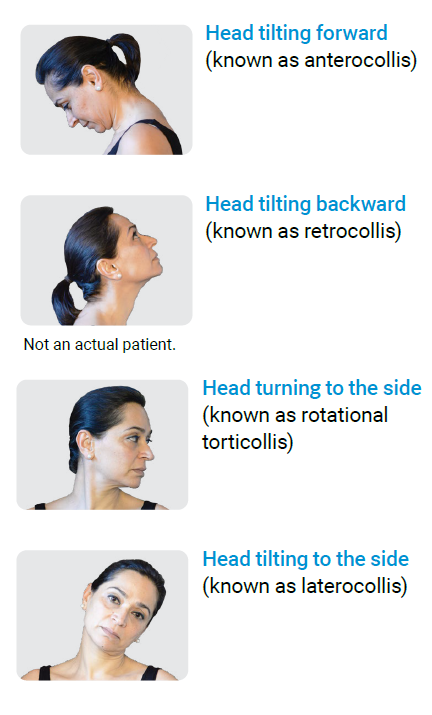
The most common form of CD is rotational torticollis, but it is common to have a combination of different position types.
Don’t wait to talk to your doctor
Be sure to tell your doctor about all the symptoms you’ve been having, including:
- Continuous contractions or sudden spasms
- Abnormal neck and head positioning
- Pain and difficulty doing activities you were able to do before
It’s important to discuss your symptoms with your doctor, whether or not you are currently experiencing them.
Causes of CD
What causes cervical dystonia?
There is no known cause of cervical dystonia (CD), but there may be a genetic component and some people with CD have family members who also have the condition. CD occurs when nerve signals in the brain tell the muscles in your neck to tighten or spasm. Sometimes, CD may develop after a head, neck, or shoulder injury.
Managing CD
Management of Cervical Dystonia
There is no cure for cervical dystonia (CD). In some people, signs and symptoms may disappear without treatment, but recurrence is common. Treatment focuses on relieving the muscle spasms and symptoms of abnormal head position and neck pain.
Treatment with Dysport
- One of these treatments for CD is Dysport, one of the botulinum toxins available.
- Dysport is a type of medicine that is injected directly into affected muscles by a specialist. It helps to temporarily block signals from the brain that tell the affected muscles to contract or tighten, usually for months at a time.
- Response to treatment may be different for each patient, so be sure to talk to your doctor regularly during treatment.
- Talk to your doctor about your condition and whether Dysport may be an option.
Dysport significantly improved abnormal head position and neck pain
In 2 clinical studies, Dysport significantly improved abnormal position of the head and reduced neck pain at week 4. Most patients did not need additional treatment until 14 weeks, and about 25% were able to wait until 18 weeks.
Based on studies of patients with CD, at least 12 weeks should pass between treatments with a botulinum toxin
Most common side effects of Dysport in adults with cervical dystonia include:
muscle weakness, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, injection site discomfort, tiredness, headache, muscle pain, problems speaking, injection site pain, and eye problems.


